Brexit – How does it affect India, Britain and the World?
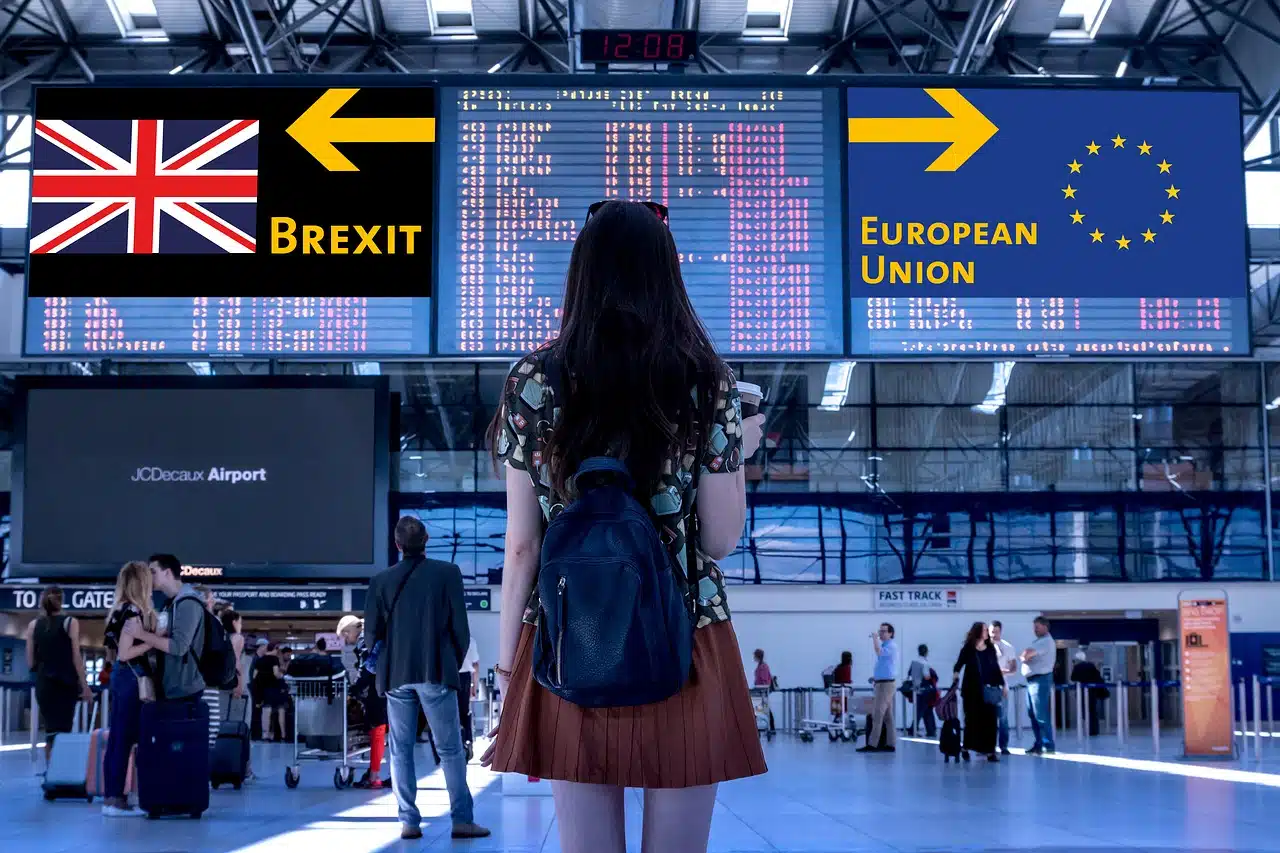

What is Brexit?
Brexit is a word used to say the UK leaving the European Union (EU). The word came up by merging the words Britan and Exit. A similar term Grexit was coined before when Greece wanted to exit from the European Union.
The European Union
The European union, commonly known as the EU founded in 1957 after the second world war. The EU is an economic and political partnership of 28 countries which aims to foster economic cooperation. Although there are 51 nations in the Europe, 28 nations have signed a treaty to become the part of the EU. Therefore, its clear that there are other European countries which are not members of the EU.
The EU has its own parliament that sets various rules for its member states in a wide range of areas including environment, transportation, consumer rights and even mobile phone charges. Eueropean Union Parliament is in Brussels.
The EU has its own currency, the euro used by 19 member countries. Those 19 countries that use the euro as currency comprise of the Euro Area (EA) or the Euro Zone. Hence, it is evident that not all EU members have the euro as currency. For example, although the UK is a member of EU, it does not use the euro so it is not a part of EA and the country has its own currency, the Pound Sterling.
The EU is a single market which allows the movement of goods and people around. It is the largest trade agency across the globe surpassing the US.
In 2012, the EU won the the Nobel Prize for Peace recognizing the organizations contribution for promoting peace, reconciliation, human rights and democracy in Europe.
Referendum on Brexit
A referendum- a vote in which everyone or nearly everyone of voting age can take part in it. A referendum held on 23rd June, 2016 to decide whether Britain should remain or leave the EU. The referendum turnout is 71.8% which is more than 30 million voted. 51.9% of people were in favor to leave the European Union while 48.1% people opposed to leave the EU.
Voting breakdown across the UK
53.4% of people in England voted for Brexit whereas, 46.6% of people were against Brexit. Wales also voted similarly with 52.5% and 47.5% respectively for and against Brexit.
However, Scotland and Northern Ireland opposed the proposal of leaving the EU. Scotland supported to remain in the EU 62% to 38%. Likewise, 55.8% in Northern Ireland backed to remain the EU and 44.2% voted to leave.
Why Britain want to leave the EU?
There are three main reasons behind the ’Leave EU Campaign’ and the issues are economics, immigration and identity.
- Economics Reasons: every week the UK sends millions of Pounds to Brussels, the headquarters of the EU. The money then gets redistributed to various member states. The supporters of the ’Leave Campaign’ argues that, the UK is losing out a big deal by staying in the EU.
- Immigration: any citizen of an EU nation can relocate and work in the UK without requiring a work visa. Although this is highly beneficial the UK economy, the right wingers complain that the non UK nationals are using up scarce public resources such as the NHS and welfare.
- Identity: the question of British identity is a complicated one while within the EU because the people in the UK do not generally consider themselves as European .As a member state of EU, Britain should abide by various policies and rules. The leavers believe that Brexit would allow to the UK to take back its laws.
But those who oppose Brexit argue that the UK is the ultimate gainer if the country stays in the EU. Further they warn that leaving the EU might crash out the UK economy and even the world economy.
How the United Kingdom is going to implement Brexit?
The Britons voted to exit from the European Union and here the question arises about the implementation process of Brexit. It reflects Britain’s future relationships with other EU nations, trade negotiations and border checks. The triggering of Britain’s exit from the European Union had started two years before in March 2017. Despite this, speculation remains about the type of relationships the UK will develop with other EU nations after they leave the bloc. Although there isn’t a clear definition yet, it can be loosely categorised as a “hard” or “soft” Brexit.
Hard Brexit: favoured by ardent Brexiters, a hard Brexit would give up Britain’s full access to the single market and full access of customs union with the EU. The hard Brexit would allow Britain full control over its borders, making new trade deals and applying laws within its territory. The UK would fall back on World Trade Organization (WTO) rules for its future trades with its former EU partners.
Pros and cons of Hard Brexit
Hard Brexit would benefit the UK by making it a global trading nation.
However, a hard Brexit could subject to tariffs for British goods and services for example, the cost of exported cars may rise. While some sectors like agriculture would lose protections against cheap imports from abroad. A significant increase in bureaucratic checks on goods passing through ports and airports is another negative impact of leaving the customs union.
Soft Brexit
This approach would make the UK’s relationship with the EU as close as possible with existing arrangements. This is supported by many Remainers.
Britain would no longer a member of EU and there won’t be a member from the UK in European Council. UK will lose its MEPs and European Commissioner. However, the country will have unrestricted access to the European single market. This enables the free trading of goods and services with the remaining EU nations. Such a tariff free selling of goods would help financial firms to operate their branches in the EU and “passporting” rights to sell the services. The UK will remain within EU’s customs union without subjecting to border checks for their exports.
Examples of this kind of deal include Norway, Iceland and Liechtenstein which are not EU members but have single market access by being part of the European Economic Area. In return these nations must make payments into EU budgets and accept four freedoms of movement of goods, services, people and capital. Further they are subject to follow EU law through the EFTA Court. Switzerland also has a similar arrangement.
Pros and cons of Soft Brexit
Experts warn that London’s position as a financial hub may face a severe blow if the UK leaves the single market. Moreover hard Brexit can create a period of economic disruption which is likely to affect Pound negatively.
No deal Brexit
A no deal Brexit means the UK will leave the European Union on 29th March 2019 without any agreements in place about the future relationships and transition periods. A transition period refers to a period of time after 29th March to 31st December,2020 to get everything in place and allow trade and people to prepare for the moment until post Brexit new rules are formed between the UK and the EU. Free movement will be continued during the transition period. The transition period happens only if the UK and the EU agree a Brexit deal.
Article 50 of the Lisbon Treaty
It sets out how an EU nation might voluntarily leave the union. It specifies that a leaver nation should notify the European Council of its intention negotiate a deal on its withdrawal and establish legal grounds on future relationships with the EU.
Impact of Brexit on Britain
- Economic and political fragmentation: UK economy would suffer a significant fall in the output. In other words, the nation’s economy may shrink between 3.8% and 7.5% by 2030. The Pound is predicted to decline by around 20%.
- Increase in the number of tourists and students: as the Pound will decline, more people across the globe will visit Britain. Similarly, more foreign students will enrol to UK universities as the cost of education will be cheaper.
- Lower immigration: EU nationals in Britain need to upgrade their immigration status. In other words, EU nationals cannot come to the UK without having proper visas.
- Trade deals: the UK can easily make trade deals with other nations like the US, Australia or India.
- Independence of action: Britain can make own policies regarding border checks and trade deals when the nation exit from the EU. Such move is argued by some that implementing a stronger border checks increases the safety of people in the UK and can limit terrorism to a certain extent.
Impact of Brexit on Global Economy
The Brexit can encourage other EU skeptic nations especially in Eurozone of the EU .Other exit referendums may arise in the coming years. The UK itself may face additional exit referendum from Scotland.
A sharp and sustained rise of the US dollar against euro will put pressure on the weak US manufacturing sector.
British – EU divorce will push the capital away from the region towards other safe destinations such as the US or Japan. This can lower interest rates and can lead to a rise in relative currency values.
A negative impact on the US and Japanese export sectors due to a higher US dollar and Japanese yen. Further for Japan, such scenario will be a blow to Japanese efforts to reinflate the economy after years of deflation.
A higher rate of the US dollar would put extra pressure on China to devalue yuwan. This in turn can negatively affect the growth rates.
Negative Impact of Brexit on India
Relocation of many Indian business firms from London to other locations. Britain always acted as a gateway to the EU. Many Indian businesses have offices in Britain so benefits can be availed and continue to remain as a part of EU. With Brexit this benefit will be taken away and eventually relocating the offices to other destinations. For example, Jaguar Land Rover a company owned by the Tata group has already started to reduce the number of employees. Similarly, there are about 800 Indian owned companies in the UK that made investments aiming a wider European markets. Because of Brexit, all of these organizations are forced to reduce their shares and changing to other destinations.
Pharmaceuticals, automobile and IT sectors would be the most affected. In short term the Brexit effect will be felt on $108 billion Indian IT sector. However, these can be covered up in long term by re-negotiations, alternative arrangements between the nations and devaluation of the value of Pound.
A reduction in sales in automobile industry and enterprises that derive good revenues from Britain could have a negative impact.
Increase in gold prices. The decision of the UK to exit from the EU has forced many to sell their risky assets and rush safe heaven investments such as gold which ultimately leads to an increase in gold price.
Also read: Everything about Kigali Agreement
Positive Impact of Brexit to India
Brexit will help to strengthen ties with the UK in long run. Because India’s still focus on innovation and entrepreneurship makes an attractive destination for investment
The UK is one of the biggest educational hubs for Indians. But due to a higher Pound value and lack of scholarships make it difficult for many Indian students to do their post graduation or doctorate degrees from the UK. Before Brexit, the British universities were forced to offer subsides and scholarships to UK citizens and EU nationals. But after Brexit, more funds should be allocated to other students and Indians can take advantage of it.
Reduction of Pound value will make Britain a good travel destination for Indians as it can reduce the travel cost.












Leave a Reply